Acrylonitrile Butadiene rubber
INTRODUCTION
NBR also termed nitrile rubber,is an emulsion co polymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene. Acrylonitrile content varies from 18 to 50%. Acrylonitrile functionality imparts excellent fuel and oil resistance.with increased acrylonitrile content there is an increase in Tg reduction in resilience, less die swell, decreased gas permeability,increased heat resistance and increased strength.because of unsaturation in butadiene portion. NBR is susceptible to small amounts of polyvinyl chloride.
The list of NBR Suppliers Across the world are listed below
S.NO
|
COMPANY
|
SYMBOL
|
TRADE
NAME
|
COUNTRY
|
1
|
Zeon corporation
|
ZECO
|
Nipol
|
Japan
|
2
|
Zeon Corporation LP
|
ZCLP
|
Nipol
|
USA
|
3
|
Zeon Chemicals Europe Ltd
|
ZCE
|
Breon Nipol
|
Wales
|
4
|
Sibur Voronezhsyntezkauchuk
|
SIBUR
|
Nitrilast
|
Russia
|
5
|
Sibur Krasnoyarsky Zavod
|
SIBUR
|
SKN
|
Russia
|
6
|
Polimeri Europa
|
Polimeri
|
Euprone N
|
Italy
|
7
|
Dwory SA
|
Dwory
|
KER
|
Poland, Oswiecim
|
8
|
Carom SA
|
CO
|
CAROM
|
Romania
|
9
|
Eliokem Chemicals
|
Eliokem
|
Chemigum
|
France,USA
|
10
|
Hyundai Petrochemical
|
Hyundai
|
SEETEC
|
Korea
|
11
|
INDUSTRIES NEGROMEX SA
|
N
|
EMULPRENE
|
MEXICO
|
12
|
JSR CORPORATION
|
JSR
|
JSR
|
JAPAN,
|
13
|
KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO
|
KKPC
|
KOSYN
|
KOREA
|
14
|
LANXESS ELASTOMERS
|
LANXESS LE
|
PERBUNAN NT
|
FRANCE
|
15
|
LANXESS INC.
|
LANXES LINC
|
Krynac Perbunan NT
|
CANADA
|
16
|
Lanzhou Chemical Industry
|
LZCC
|
NBR
|
CHINA
|
17
|
Nantex Industry Co.Ltd
|
Nantex
|
NANTEX
|
TAIWAN
|
18
|
Negromex Industries SA de CV
|
Negromex
|
N-xxxx
|
Mexico
|
19
|
Nitriflex Industria e Comercio
|
Nitriflex
|
NITRIFLEX N
|
BRAZIL
|
20
|
ParaTec Elastomers LLC
|
Paratec
|
Paracril Paraclean Paracil OZO
|
Mexico
|
21
|
Petro China Jilin Petrochemical co
|
JIL
|
NBR
|
China,Jilin
|
Nitrile rubbers are copolymers of butadiene
and acrylonitrile which are produced by
emulsion polymerisation; ‘hot’ and ‘cold’ polymerised types are available.
The ‘hot’ polymerised types generally have higher green strength and are slightly harder to process than ‘cold’ copolymers.
The introduction of acrylonitrile into the polymer backbone imparts
oil resistance and affects many
other properties. Grades which vary in acrylonitrile (ACN) content from 18-50% are commercially available, the percentage of acrylonitrile present forming the basis of the following grade descriptions:
Low
|
18-24%
|
ACN
|
Medium low
|
26-28%
|
ACN
|
Medium
|
34%
|
ACN
|
Medium high
|
38-40%
|
ACN
|
High
|
50%
|
ACN
|
USES:
Common applications for NBR take advantage of the chemical resistance of the rubber.
Seals, O-rings, gaskets, oil field parts, diaphragms are the principal uses of NBR. Gloves,
pump stators, belts, wire and cable insulation, hose tubes/covers, rolls, sound insulating
gaskets, footwear/shoe products, and miscellaneous moulded rubber goods are some of
the minor applications. Nitrile rubber is also used for modification of plastics, adhesives
coatings, and friction materials.
Mooney Viscosity
chemist with a broad choice of rheological properties to meet any process conditions and
compound design. The higher the loading of both filler and plasticizer the higher the
viscosity needed for satisfactory uncured strength.
The vast majority of NBR is produced by ‘‘cold polymerization,’’ which gives a
more linear polymer with better processing properties. Hot polymerized elastomers
are tougher due to more branching, which results in compounds with higher green
strength, and these may require more care in handling. They will build up more heat
in processing, hence are more scorchy. Branching may also lead to polymers with a
un desired high amoun t chain entang lemen t, b ut h igh loadings of fi ller and plast icizer
wi ll help to alle viate the problem. So me grades of hot polymers b y design have
cross link ed domai ns know n a s gel. The se are most often blende d wi th other nitr ile
grades for imp roved green stre ngth and dime nsional stability.
Hot polym erized NBR is often used in solve nt adhesi ves because of the better
green stre ngth.
Specific Gravity
The specific gravity of NBR ranges from 0.94 for polymers in the 17%–20% ACN
content range up to 1.02 for a 50% ACN type.
STABILIZER:
The stabilizer or anti oxidant added during polymerization functions as a control of oxidation during drying of the polymer and in storage. A non staining type is often used to allow the NBR to be used in light-colored articles and in contact with various surfaces without causing staining or certain types that prevent the crazing of plastic. Staining stabilizers generally exhibit better protection in storge.
A stabilizer that inhibits free radical formation in processing and storage of the NBR and uncured
compound helps in preventing an increase in viscosity of the polymer and compound.
The stabilizer is not intended to provide protection of the vulcanized part, hence
antioxidants or antiozonants are needed in the compound design to achieve satisfactory
service life
Mixing and Processing:
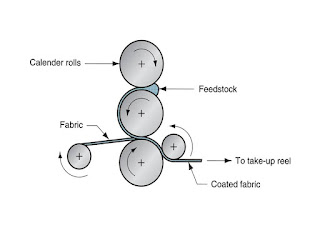
All of the commercially available Nitrile rubber can be mixed either on a two roll mill or internal mixing equipment.Compounds can be designed to be easily extruded, Calendered or moulded with injection, Compression or transfer techniques.
Mooney Viscosity
- Standard nitrile elastomers range in Mooney viscosity from 26 to 120 thus providing the
chemist with a broad choice of rheological properties to meet any process conditions and
compound design. The higher the loading of both filler and plasticizer the higher the
viscosity needed for satisfactory uncured strength.
- This approach is commonly used in hose and tubing, which requires good ‘‘green strength’’ to maintain shape, size, and toresist imbedding of reinforcing filaments in the tubing. If a compound design is based on a high filler loading but a low plasticizer content, a low-viscosity polymer is needed.
- In addition, if injection or transfer molding is employed to produce the part then again a low viscosity is needed. It should be noted that higher molecular weight NBR will provide better physical properties and lower compression set.
The vast majority of NBR is produced by ‘‘cold polymerization,’’ which gives a
more linear polymer with better processing properties. Hot polymerized elastomers
are tougher due to more branching, which results in compounds with higher green
strength, and these may require more care in handling. They will build up more heat
in processing, hence are more scorchy. Branching may also lead to polymers with a
un desired high amoun t chain entang lemen t, b ut h igh loadings of fi ller and plast icizer
wi ll help to alle viate the problem. So me grades of hot polymers b y design have
cross link ed domai ns know n a s gel. The se are most often blende d wi th other nitr ile
grades for imp roved green stre ngth and dime nsional stability.
Hot polym erized NBR is often used in solve nt adhesi ves because of the better
green stre ngth.
Specific Gravity
The specific gravity of NBR ranges from 0.94 for polymers in the 17%–20% ACN
content range up to 1.02 for a 50% ACN type.
The stabilizer or anti oxidant added during polymerization functions as a control of oxidation during drying of the polymer and in storage. A non staining type is often used to allow the NBR to be used in light-colored articles and in contact with various surfaces without causing staining or certain types that prevent the crazing of plastic. Staining stabilizers generally exhibit better protection in storge.
A stabilizer that inhibits free radical formation in processing and storage of the NBR and uncured
compound helps in preventing an increase in viscosity of the polymer and compound.
The stabilizer is not intended to provide protection of the vulcanized part, hence
antioxidants or antiozonants are needed in the compound design to achieve satisfactory
service life
Mixing and Processing:
All of the commercially available Nitrile rubber can be mixed either on a two roll mill or internal mixing equipment.Compounds can be designed to be easily extruded, Calendered or moulded with injection, Compression or transfer techniques.

Comments
Post a Comment