Elastomeric Bearings: Plain and Reinforced
Plain, unreinforced elastomeric pads are used for short spans on which loads and
movements can be accommodated by a single layer of elastomer.
As vertical load and movement requirements increase, thin reinforcing plates are
combined with multiple layers of elastomer to form a laminated reinforced elastomeric
assembly
. Steel and fiberglass reinforcement layers have been used;
however, fiberglass is weaker, more flexible, and does not bond as well to the elastomer
as does steel reinforcement. As a result, the use of thin steel-plate reinforcement has
become more common.
Neoprene is the most widely used elastomer, but some states also use natural
rubber particularly in colder climates, to meet AASHTO low temperature
requirements. Natural rubber generally stiffens less than neoprene at low
temperatures. Neoprene has greater resistance to ozone and a wide range of chemicals
than natural rubber, making it more suitable for some harsh chemical environments.
Cotton Duck pads
Cotton Duck Pads
Cotton duck bearing pads are another type of elastomeric bearings that are occasionally
used in some states, typically for precast concrete I-girder bridges with span lengths
up to the 150- to 180-ft range. Cotton duck pads (CDPs) are preformed elastomeric
pads consisting of very thin layers of elastomer (less than 0.4 mm [1
/60 in.]) interlaid
with cotton or polyester fabric. They are stiff and strong in compression, giving them
much larger compressive load capacities than plain elastomeric pads; however, CDP
shear deflection capability is very limited. The CDP bearings provide a high stiffness in
the direction of applied compressive force and are helpful in limiting problems encountered
during construction of heavy girders because of rotational instability, generally
observed with other elastomeric bearing types. For large shear strain, CDPs may split
and crack or result in girder slip on the CDP. The limited shear deflection capacity is
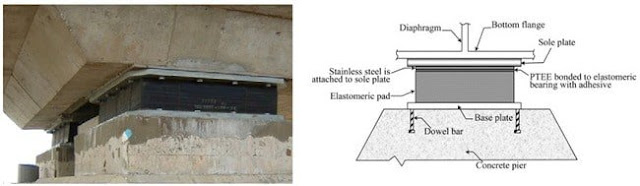
frequently overcome by the addition of a polytetrafluorethylene (PTFE) sliding surface
to accommodate large movement. When PTFE surfaces are used, they are often combined
with stainless steel sliding surfaces, similar to that shown in Figure 10.2. The
overall capacities depend on the stiffness and deformation capacity of the CDP and
vary from manufacturer to manufacturer. To assure adequate performance from CDP,
quality control (QC) testing measures and design recommendations have been developed
and incorporated into the LRFD specifications


Nice blog, thanks for sharing Combined Bearing
ReplyDeleteGreat insights! Unick Vibration also offers reliable Anti Vibration Elastomeric Pads that enhance industrial stability and performance across multiple applications.
ReplyDelete