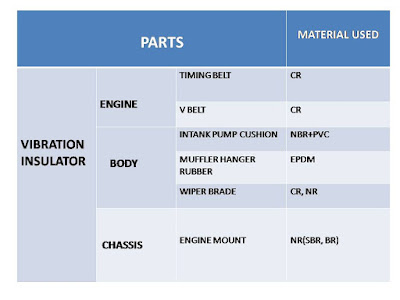
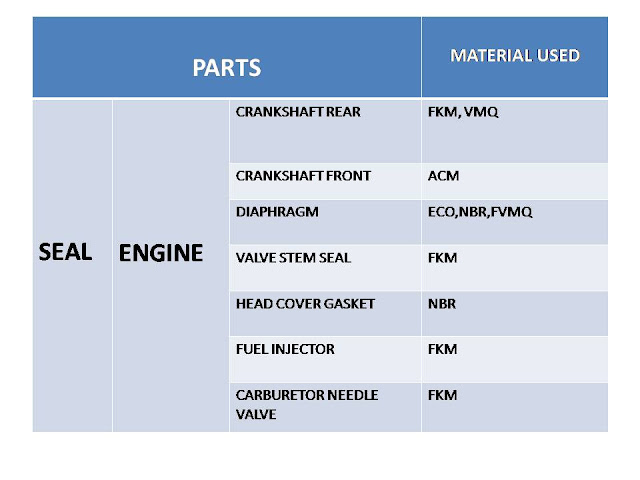
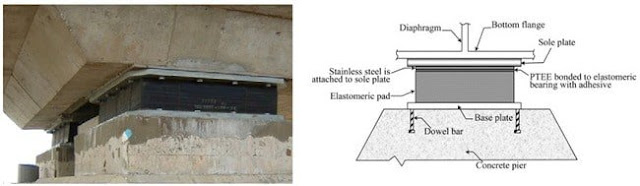
Rubber Terminologies - A
A AAS : Atomic absorption spectroscopy Ablation : Literally removal but applied particularly in space technology to the process of using up the frictional heat developed on re entry of the vehicle into the earth atmosphere by degradation of the heat shield. ACM :An abbreviation for acrylic rubber Accelerator: A substance which fastenes the vulcanization of an elastomer,causing it to take place in a short time or at a lower temperature. Abrasion : The wearing away of a surface in service by mechanical action,such as scrapping or erosion. Abrasion Tester : A machine for determining the quantity of material worn away by friction under specified conditions. Abrasion Resistance Index : A measure of the abrasion resistance of a rubber relative to that of a standard rubber under the same specified conditions, expressed as a percentage. Absorption : The physical mechanism by which one substance takes up another substance (liquid, gas or vapor) into its in