Rubber Terminologies - A
A
AAS: Atomic absorption spectroscopy
Ablation: Literally removal but applied particularly in
space technology to the process of using up the frictional heat developed on re
entry of the vehicle into the earth atmosphere by degradation of the heat
shield.
ACM:An abbreviation for acrylic rubber
Accelerator: A substance which fastenes the
vulcanization of an elastomer,causing it to take place in a short time or at a
lower temperature.
Abrasion:The wearing away of a surface in service by
mechanical action,such as scrapping or erosion.
Abrasion Tester: A machine for determining the quantity of material worn away by friction under specified conditions.
Abrasion Resistance
Index : A
measure of the abrasion resistance of a rubber relative to that of a standard
rubber under the same specified conditions, expressed as a percentage.
Absorption
: The
physical mechanism by which one substance takes up another substance (liquid,
gas or vapor) into its interior.
Accelerator
: A compounding
material used in small amounts, with a vulcanizing agent, to increase the speed
of vulcanization.
Acid
resistance: Withstand the action of
acid.
Accelerated
Life Test : Any set
of test conditions designed to reproduce, in a short time, the deteriorating
effect obtained under normal service conditions.
Accelerated
Service Test : A service or
bench test in which some service condition, such as speed, temperature or
continuity of operation, is exaggerated in order to obtain a result in shorter
time.
Adhesives:Polymeric materials are commonly used for
bonding materials. Impact or contact adhesives are mainly based on highly
crystalline polychloroprene (Neoprene), NR latex is used as a flexible adhesive very
suitable for use with fabrics. Rigid adhesives based on materials such as polystyrene cement,
epoxy resin or cyanoacrylates are suitable for bonding of rigid materials. The bond is
provided by intermolecular forces between the adhesive and the adherend.
Adapter: The accessory part which can complete the connection between a hose fitting
and another fluid system component. Often, a tube fitting connected to a hose assembly rather than a tube assembly.
Adhesion: Tendency of rubber to bond or cling to a
contact surface.
Adhesion failure:It is due to the following reason 1. The separation of two bonded surfaces at an interface by a force less than specified in a test method.2. The separation of two adjoining surfaces due to service conditions.
Adhesive coating: a layer applied to any product surface to increase its adherence to an
adjoining surface.
After
Cure : Continuation
of vulcanization after the desired cure is effected and the heat source removed
(also referred to as Post-Cure).
Ageing : To undergo changes in physical properties with
age or lapse of time.
Ageing,
Accelerated : Tests run on
various rubbers to find out, in as short a period as possible, the destructive
influence of light, oxygen, heat and ozone.
Ageing, Oxygen
Bomb : A means of
accelerating the change in the physical properties of rubber compounds by
exposing them to action of oxygen at an elevated temperature and pressure.
Ageing , Air
Bomb : Similar
to an oxygen bomb, but used with air.
Ageing,
air oven: The
process of exposing materials to the action of air at an elevated temperature
at atmospheric pressure
Air Spring :An inflatable bellows used in a pneumatic
suspension system for motor transport;
Allotropy: Many elements including sulphur, carbon and
oxygen can exist in two or more forms with different
physical, and often chemical, properties; such elements are said to exhibit
allotropy and the different forms are known as allotropes or allotropic
forms.
Antioxidant: An organic substance which inhibit or retards
oxidation.
Angle of Lay: The angle developed at the intersection of a structural element and a line parallel to its lineal axis
Antiozonant: A substance that retards or prevents the
appearance of cracks from action if ozone when the elastomer is exposed under
tension to air containing ozone.
Aniline point: The lowest temperature at which equal volume of
pure,fresh Aniline and oil will completely dissolve in one another is the
Aniline point of the oil.
Anticoagulant:Any substance used to prevent coagulation of
rubber latex, the common most are ammonia, sodium sulphite and formaldehyde.
Anti-Extrusion Ring or
Device: A washer like
device of a relatively hard material placed in the gland between the o-ring and
groove side wall also called a back up ring.
Antiflex
cracking agent: A
compounding material used to retard cracking caused by cyclic deformations.
Antirad: A compounding ingredient added to elastomer to
increase their resistance to ionising radiation
AP: Abbreviation for ammonium Polyphosphate
Aromatic Oil: A hydrocarbon process oil
containing at least 35%, by mass, of aromatic hydrocarbons.
Aramid Fibers: A class of heat resistant and strong synthetic fibers in which the chain molecules are highly oriented along the fiber axis so the strength of the chemical bond can be exploited.
Armor: A protective cover slid over and affixed to a hose assembly used to prevent over bending or for the purpose of protecting hose from several external environmental conditions such as hot materials, abrasion or traffic.
ASTM Interantional: Formerly known as the American Society
for Testing and Materials ASTM International is a global standards organization that developes
international standards for materials, products, systems, and services.
The current Annual Book of ASTM Standards has 15 sections covering
subjects ranging from steel, plastic, & rubber to electrical, water,
nuclear and more.
Atmospheric aging
resistance: Loss of physical
properties due to the normal action of its surroundings
Atmospheric Cracking: Cracks produced in the surface of rubber
articles by exposure to atmospheric conditions.
AU: Abbreviaiton for polyester type Polyurethane
rubbers.
Air Checks – The surface markings of depressions due
to trapping air between the product being cured and the mold or
press surface.
Air curing: Vulcanization of a rubber product in
air,as distinguished from in a press or steam vulcanizer.
Autoclave:A pressure vessel constructed of steel used for
the vulcanisation of rubber products by the
Axial Seal: An o-ring that seals on a plane
perpendicular to its axis.
Axial Movement: Compression or elongation along the longitudinal axis.
AZDN: Azobiz-isobutyronitrile,Blowing agent
ACM:An abbreviation for acrylic rubber
Abrasion Tester: A machine for determining the quantity of material worn away by friction under specified conditions.
Adapter: The accessory part which can complete the connection between a hose fitting
and another fluid system component. Often, a tube fitting connected to a hose assembly rather than a tube assembly.
Adhesion failure:It is due to the following reason 1. The separation of two bonded surfaces at an interface by a force less than specified in a test method.2. The separation of two adjoining surfaces due to service conditions.
Adhesive coating: a layer applied to any product surface to increase its adherence to an
adjoining surface.
Angle of Lay: The angle developed at the intersection of a structural element and a line parallel to its lineal axis
Aramid Fibers: A class of heat resistant and strong synthetic fibers in which the chain molecules are highly oriented along the fiber axis so the strength of the chemical bond can be exploited.
Armor: A protective cover slid over and affixed to a hose assembly used to prevent over bending or for the purpose of protecting hose from several external environmental conditions such as hot materials, abrasion or traffic.
Axial Movement: Compression or elongation along the longitudinal axis.
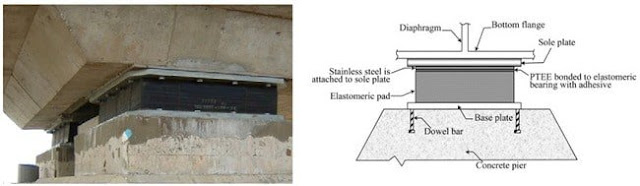
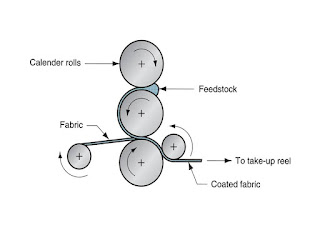

Comments
Post a Comment